Cortical Glutamatergic Neurons
Origin: Human iPSC line
Products
5M Viable Cells/Vial - Standard (BX-0300)
1M Viable Cells/Vial - Standard (BX-0300e)
2M Viable Cells/Vial - GFP expressing (BX-0301)
Contents: 1 vial of cells and corresponding BrainXell supplements
Cryopreserved
Discount Pricing for Academics
Request Quote for Larger orders or Custom Service
Specifications
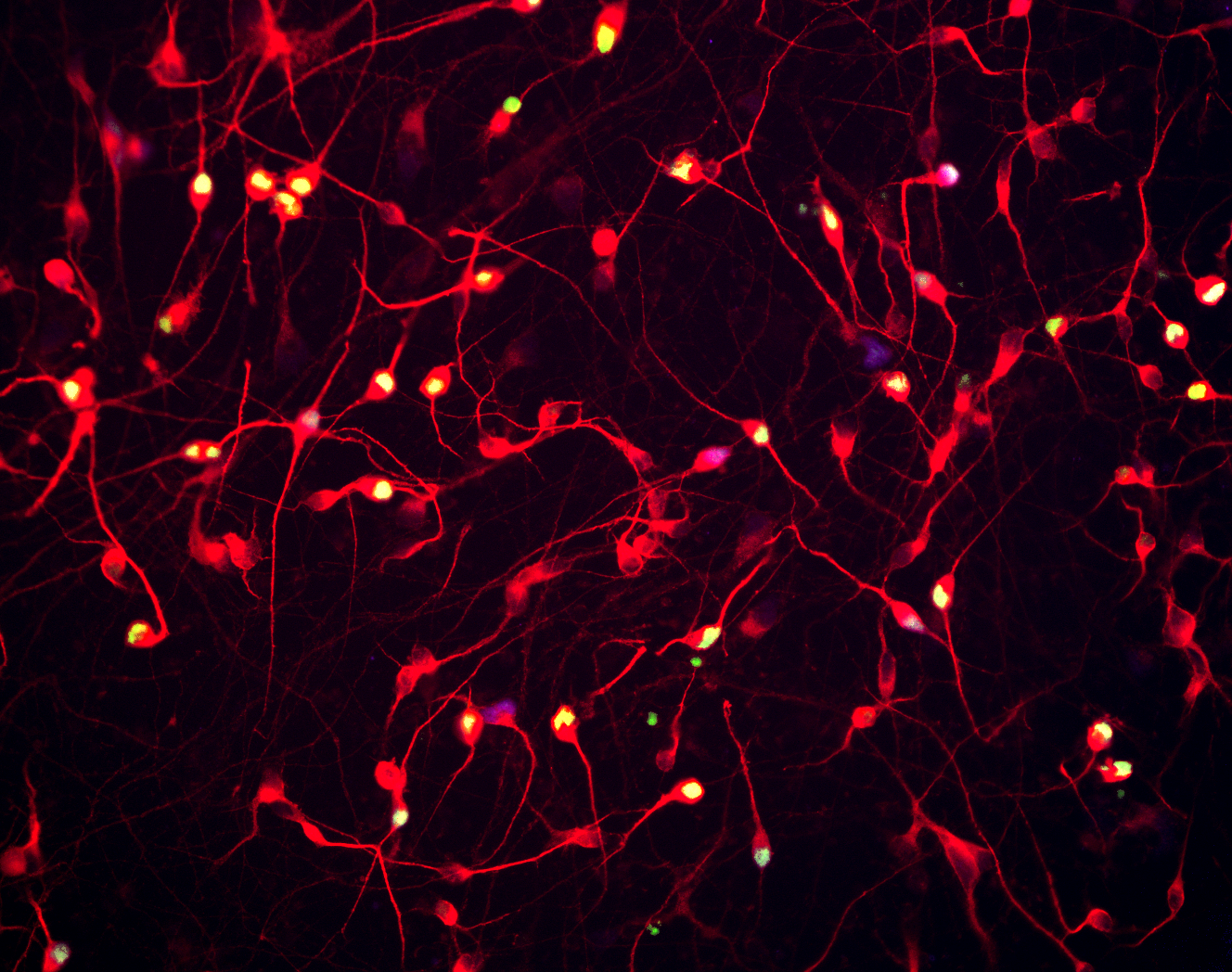
Marker Expression: Cortical Glutamatergic Neurons (BX-0300) have high neuronal purity (>90%) and comprise predominantly excitatory neurons. Labeling with the pan-neuronal marker MAP2 (red) highlights the neuronal purity of these cells. Labelling with the glutamatergic-specific markers CTIP2 (green) and TBR1 (blue) indicates overwhelming presence of glutamatergic neurons.
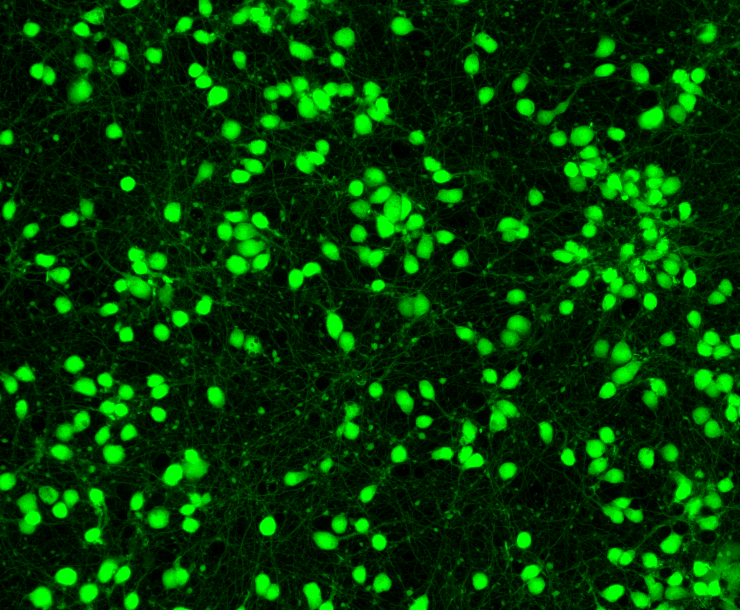
Morphology: Cortical Glutamatergic Neurons (BX-0300) exhibit substantial neurite outgrowth within a week in culture and are adherent. Calcein staining (green) demonstrates the characteristic oval cell shape and long processes of Cortical Glutamatergic Neurons in culture.
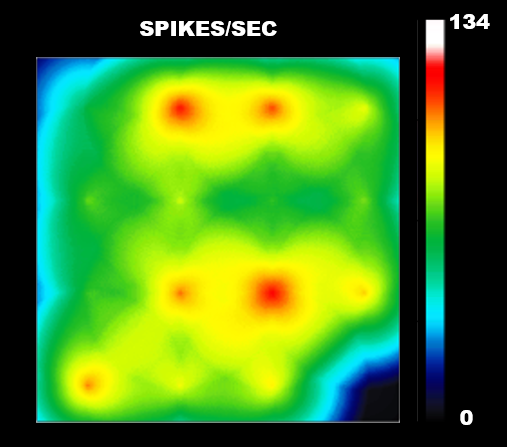
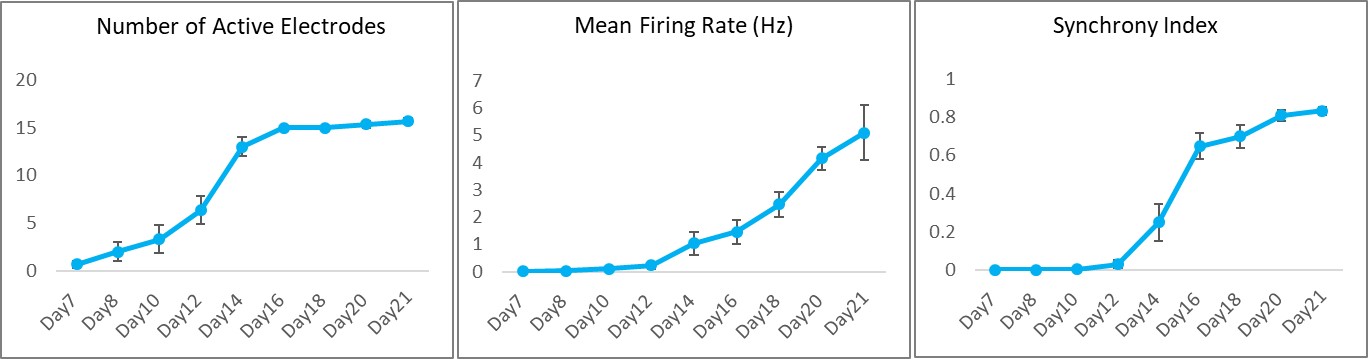
Function: Cortical Glutamatergic Neurons (BX-0300) exhibit pronounced electrophysiological activity after two weeks in culture, as demonstrated by multi-electrode array (MEA) recordings.
Protocols
Recommended protocols developed by BrainXell utilize proprietary supplements that are included with each purchase of neurons. The recommended protocol will depend on the application. Contact BrainXell application scientists to learn more.
Applications
Calcium Influx Assays:
Changes in calcium concentration are closely tied to neuronal activity as action potentials are associated with large pre-synaptic calcium influx and a notable rise in postsynaptic calcium at excitatory synapses. This can be observed experimentally by stimulating the neurons or culturing the neurons under suitable conditions to form mature networks that exhibit spontaneous oscillations. The influx of calcium can be measured using a variety of calcium-sensitive fluorescent dyes, which are commercially available.
Cortical Glutamatergic Neurons (BX-0300) were cultured in 96-well plates for three weeks and then loaded with Calbryte-520 (AAT Bioquest). Spontaneous oscillations were recorded in all wells simultaneously using an FDSS/µCell Functional Drug Screening System (Hamamatsu).
MEA Assays:
Multi-electrode arrays (MEA) measure extracellular voltage changes that occur as neurons fire action potentials. These measurements reveal the firing patterns of individual neurons as well as the patterns of neuronal networks that exist in the cell culture. Such measurements are non-invasive and allow for repeated recordings.
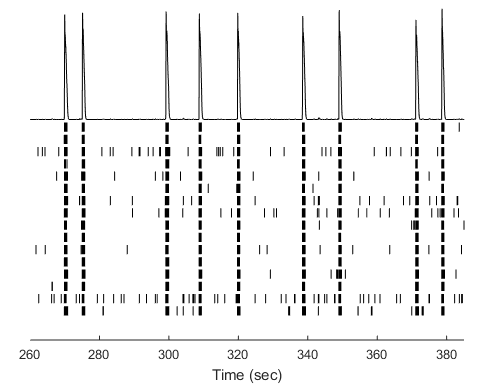
Cortical Glutamatergic Neurons (BX-0300) were cultured on Axion Biosystems MEA plates for several weeks and recorded regularly. Below, a time course of the number of active electrodes, mean firing frequency, and synchrony index reveal the development of neuronal activity in the glutamatergic neurons over several weeks in culture.
The raster plot of spike activity shows network bursting observed on day 21 for Cortical Glutamatergic Neurons.
Read More About BrainXell’s Cortical Glutamatergic Neurons: